-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Surfaces
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Surfaces
nanoCAD allows you to create a polygon or polyface mesh by specifying vertices. The mesh density controls the number of facets in legacy polygonal and polyface meshes. Density is defined in terms of a matrix of M and N vertices, like a grid consisting of columns and rows. M and N specify the column and row position, respectively, of any given vertex.
The mesh density (i.e., the number of its edges) is set by the product (M-1) × (N-1), where M is the number of vertices along the first direction, and N is the number of vertices along the second direction (directions are called the M-direction and N-direction). The position of any vertex in the network is determined by two indices, similar to the row and column numbers in the matrix. When modeling with the help of three-dimensional networks, not only the edges of a three-dimensional object are described, but also its faces. Using meshes, you can get an approximation of curved surfaces with a given accuracy.
Mesh objects do not have the mass and volume properties of 3D solids.
In the ribbon tab 3D Tools – Meshes, as well as in the Draw menu – Meshes item of the classic interface, the commands for the 3D meshes creation in the form of elementary surfaces are presented – box, wedge, cone, sphere, torus, pyramid, dish, dome, as well as in the form of uniform and non-uniform meshes indicating the number of nodes.
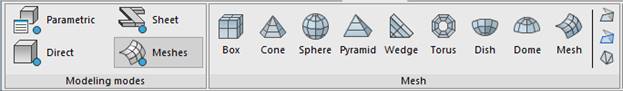
note: These objaects are of Sub Mesh, Polyface Mesh or Polygonal Mesh type
You can control whether the mesh is displayed as a wireframe, hidden, or conceptual image by changing the visual style.


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt 
