-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Modify dimension style
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Modify dimension style
In the "Modify dimension style" dialog, properties for a new style are set and parameters of an existing one are edited.
This dialog is called when you click the "Modify..." or "Override..." buttons from the "Dimension Style Manager", as well as from the "Creating style" window.
The name of the edited style is reflected in the title of the dialog.
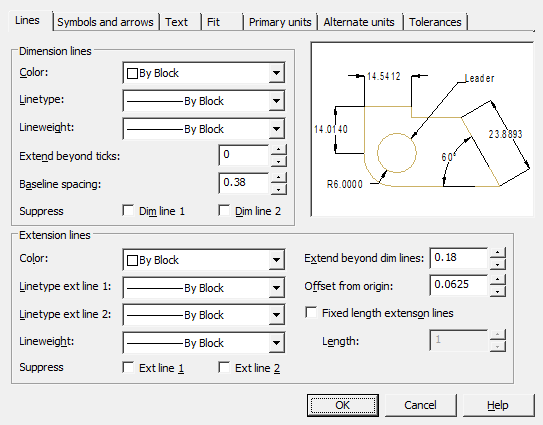
Dialog "Modify dimension style" contains tabs:
- Lines
- Symbols and arrows
- Text
- Fit
- Primary units
- Alternate units
- Tolerances
The model image on each tab shows a preliminary result of the property changes.
Tab Lines
Sets the format and properties of dimension lines, extension lines, arrows, and center marks.
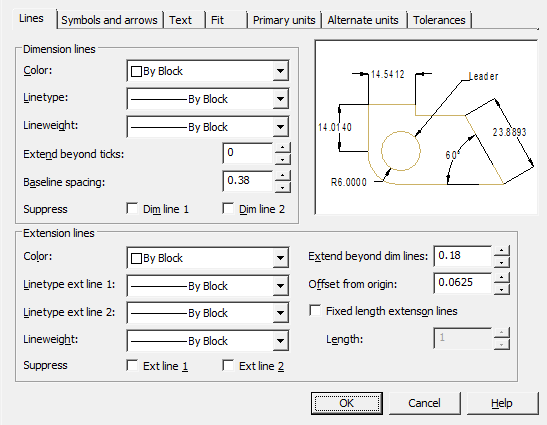
Simension lines
Color – setting the color of dimension lines.
Linetype – setting the dimension line type.
Lineweight – setting weights for dimension lines.
Extend deyond ticks – when using serifs as dimension arrows, setting the distance the dimension line should extend beyond the extension lines.
Baseline spacing - setting the distance between dimension lines in dimensions from a common base.
Suppress – sets the suppression of the display of dimension lines if they go beyond the extension lines.
- Dim line 1 – suppress the first dimension line.
- Dim line 2 – suppress the second dimension line.
Color - setting the color of the extension lines.
Linetype ext line 1 – setting the type of the first extension line.
Linetype ext line 2 – setting the type of the second extension line.
Lineweight – setting weights for extension lines.
Suppress – set to suppress extension lines:
- Ext line 1 – suppress the first extension line.
- Ext line 2 – suppress the second extension line.
Extend beyond dim lines – setting the distance that extension lines should protrude beyond the dimension line.
Offset from origin – sets the distance by which extension lines deviate from object points.
Fixed length extenson lines - sets the full length of the extension lines from the dimension line to the origin of the dimension.
Tab Symbols and arrows
Sets the format and position of arrows, center marks, arc length symbols, and radius dimension polylines.
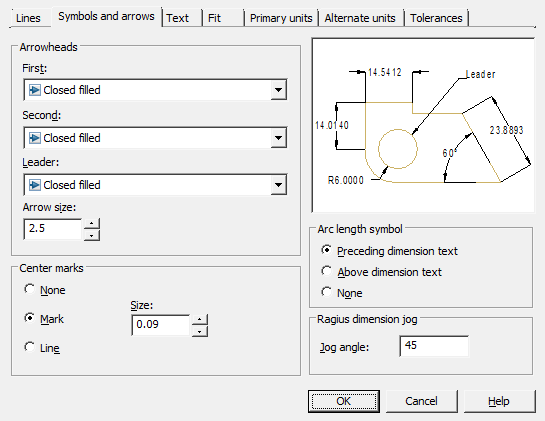
Arrowheads
Controls the appearance of dimension arrows.
First – selection of the arrow type for the first dimension line. When you change the type of the first arrow, the type of the second is automatically changed.
Second – selection of the arrow type for the second dimension line.
Leader – setting the arrow type for the leader.
Arrow size – displaying the existing one and setting a new size for the arrows.
Center marks
Controls the placement of center marks and centerlines when placing a diameter or radius.
None - do not create center mark and centerlines.
Mark - create a center mark.
Line - create centerlines.
Size - displays an existing one and sets a new size for the center mark or centerline.
Arc length symbol
Controls the display of the arc symbol in the arc length dimension.
Preceding dimension text - inserts arc length characters before dimension text.
Above dimension text - inserts arc length characters above dimension text.
None - prohibiting the display of arc length symbols.
Radius dimension jog
Controls the display of broken lines (zigzags) of radius dimensions, in cases where the center is located outside the page.
Jog angle - sets the angle of the perpendicular line connecting the extension and dimension lines of the radius dimension.
Tab Text
Setting the format, placement and alignment of dimension texts.
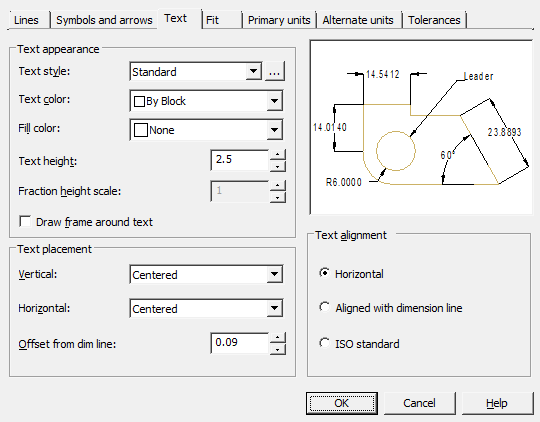
Text appearance
Text style – selects the current dimension text style from the list.
Text color – setting the color of the dimension text.
Fill color – setting the background color of the text in dimensions.
Text height - sets the current height of the dimension text. If the text style specifies a fixed height (that is, the style's height value is not 0), then the height entered here is ignored.
Fraction height scale – setting the scale of fractional values relative to the rest of the text. This option is available if the "Unit format" is set to "Fractional" on the "Primary units" tab. The height of fractional texts is determined by multiplying the height of the regular text by a given factor.
Draw frame around text – sets the display of dimension text in a frame.
Text placement
Vertical – select the option to align the dimension text vertically relative to the dimension line:
- Centered - centered dimension text between extension lines.
- Above - positioning the dimension text above the dimension line. The distance from the dimension line to the bottom border of the text is equal to the value specified in the "Offset from dim line" option.
- Outdise - positioning the dimension text next to the dimension line on the side farthest from the first fit point.
- JIS - placement of dimension text in accordance with the requirements of Japanese industrial standards JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards).
- Below - the location of the dimension text below the dimension line. The distance from the dimension line to the top border of the text is equal to the value specified in the "Offset from dim line" option.
Horizontal – select an option to position the dimension text horizontally along the dimension line relative to the extension lines:
- Centered - centered dimension text between extension lines along the dimension line.
- At Ext Line 1 - the location of the text to the left of the first extension line. The distance from the extension line to the text is equal to the sum of twice the dimension arrow ("Symbols and arrows" tab) and the text gap (the "Offset from dim line" option).
- At Ext Line 2 - the distance from the extension line to the text is equal to the sum of twice the dimension arrow ("Symbols and arrows" tab) and the text gap (the "Offset from dim line" option).
- Over Ext Line 1 - positioning text above or along the first extension line.
- Over Ext Line 2 - positioning text above or along the second extension line.
Offset from dim line – setting the size of the current text gap (the width of the empty space around the text located at the break in the dimension line). This value is also used as the minimum length of the broken dimension line fragments.
The text is located between the extension lines only if the lengths of these fragments are not less than the size of the text gap. If text is above or below the dimension line, it will only fit between the extension lines if there is enough space for the dimension arrows and dimension text to be spaced apart by the text gap.
Text alignment
Sets the orientation of the dimension text between and outside dimension lines.
Horizontal – place text horizontally.
Aligned with dimension line – place text along the dimension line.
ISO standart - place along the dimension line if the text is inside the extension lines, or horizontally if the text is outside.
Tab Fit
Controls the position of dimension text, arrows, leaders, and dimension lines.
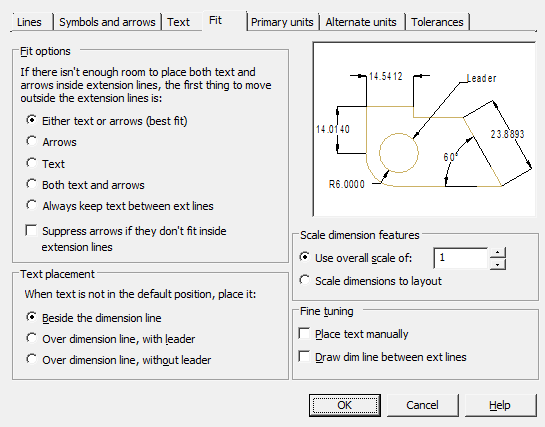
Fit options
Set the layout of text and arrows if there is not enough space between the extension lines to place them together:
Either text or arrows (best fit) - move either the text or arrows outside the dimension lines, whichever is the best location.
Arrows - move outside the extension lines, first arrows, then text.
Text - move outside the extension lines, first the text, then the arrows.
Both text and arrows - if there is not enough space, then both text and arrows are located outside the extension lines.
Always keep text between ext lines – always place text between extension lines.
Suppress arrows if they don't inside extension lines - if there is not enough space for arrows between the extension lines, they are not displayed.
Text placement
Selecting an action when the dimension text is moved from the default position (specified by the dimension style):
Beside the dimension line – the dimension line moves with the text.
Over dimension line, with leader – dimension lines do not move, but a leader is drawn that connects them and the text. The leader is not drawn if the text is too close to the dimension line.
Over dimension line, without leader – no connections are made between the text and the dimension line.
Scale dimension feature
Use overall scale of – setting the scale factor for all dimension style parameters that specify dimensions, distances and indents, including the height of the text and the size of the arrows.
Scale dimensions to layout - sets a scale factor based on the ratio of units in the current model space viewport and paper space.
Fine tuning
Place text manually – places the dimension at the point specified when prompted for Dimension line position. All horizontal placement modes are ignored.
Draw dim line between ext lines – draw dimension line between extension lines, even if dimension arrows are positioned outside of them.
Tab Primary units
Sets the format and precision of base units, and dimension text prefixes and suffixes.
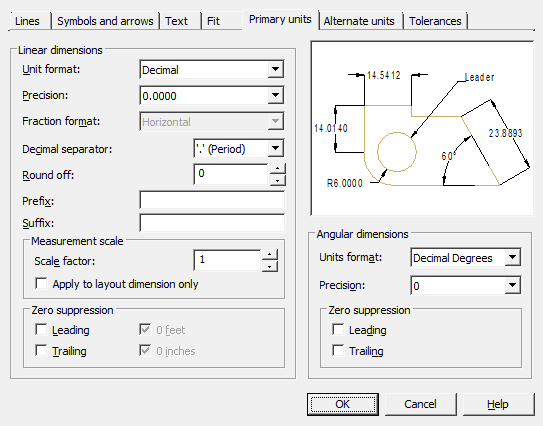
Linear dimensions
Unit format - controls the display and format of tolerances in dimension text.
Precision – setting the number of decimal places in the dimension text.
Fraction format – setting format for fractional texts.
Decimal separator – selection of separator type for sizes expressed in decimal units.
Round off – setting rounding rules for all types of dimensions, except for angular dimensions. Example: for a given accuracy of 0.25, all measured distances are rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.25. When you enter a value of 1.0, all measured distances are rounded to the nearest whole value. The number of digits in fractional parts of distances depends on the precision specified in the "Precision" field.
Prefix – defining the dimension text prefix. You can enter special characters or use control codes to display special characters. For example, the control code "%% c" matches the diameter character. An explicit prefix takes precedence over default prefixes such as those used for diameter and radius.
Suffix – definition of a dimension text suffix. You can enter special characters or use control codes to display special characters. For example, typing the suffix mm will add it to the dimension text. The suffix entered here takes precedence over the default suffixes.
Measurement scale
Scale factor – setting the scale factor for linear dimensions. It is recommended not to change the default value of 1.00. The factor has no effect on angular dimensions, rounding accuracy, positive and negative tolerances.
Apply to layout dimension only – applies a scale factor only to dimensions plotted in layout viewports. It is recommended to disable the setting.
| Important! |
Changing the value of the scale of the dimensions of a style in a customization changes the value in the dimensions of the same style that are already assigned. This bug is unrecoverable for technical reasons. |
Zero suppression - Controls the suppression of leading and trailing zeros, as well as feet and inches zero.
- Leading – suppress leading zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 0.3000 is written as .3000.
- Trailing – suppress trailing zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 11.5000 is represented as 11.5 and 30.0000 is represented as 30.
Angular dimensions
Sets the current corner format for angular dimensions.
Units format – selection of units of measure for angular dimensions.
Precision – setting the number of decimal places in angular dimensions.
Zero suppression - control of suppression of leading and trailing zeros.
- Leading – suppress leading zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 0.3000 is written as .3000.
- Trailing – suppress trailing zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 11.5000 is represented as 11.5 and 30.0000 is represented as 30.
Tab Alternate units
Setting the format and precision for alternative dimension units.
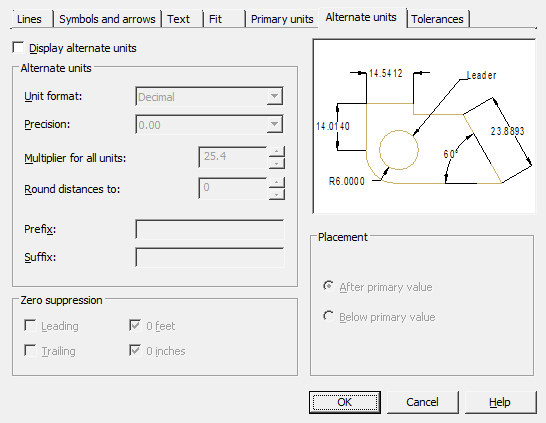
Display alternate units – inclusion of the possibility of using alternative dimensional units.
Alternate units
Unit format - setting the format of alternative units.
Precision – setting the number of decimal places after the decimal point.
Multiplier for all units - setting the conversion factor from basic units to alternative ones. Example: To convert inches to millimeters, enter 25.4. The value has no effect on angular dimensions and does not apply to rounding precision or positive and negative tolerances.
Round distances to – sets the rounding rule for all types of dimensions, except for angular dimensions. Example: when setting the accuracy to 0.25, all measured distances are rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.25. When you enter a value of 1.0, all measured distances are rounded to the nearest whole value. The number of digits in fractional parts of distances depends on the precision specified in the "Precision" field.
Prefix – defining the prefix of the alternate dimension text. You can enter special characters or use control codes to display special characters. For example, the control code "%% c" matches the diameter character. An explicit prefix takes precedence over default prefixes such as those used for diameter and radius.
Suffix – defining the suffix of the alternate dimension text. You can enter special characters or use control codes to display special characters. For example, entering the suffix mm will add it to the text. The suffix entered here takes precedence over the default suffixes.
Zero suppression
Controls the suppression of leading and trailing zeros and feet and inches zero.
Leading – suppress leading zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 0.3000 is written as .3000.
Trailing – suppress trailing zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 11.5000 is represented as 11.5 and 30.0000 is represented as 30.
Placement
Sets the position of alternate units in dimension text.
After primary value – display the value in alternate units immediately following the value in base units.
Below primary value - display the value in alternate units below the value in base units.
Tab Tolerances
Controls the display and format of tolerances in dimension text.
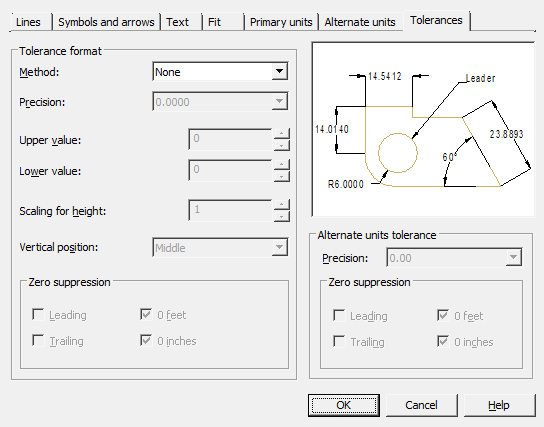
Tolerance format
Method – choice of method for determining tolerances.
| None- disable display of tolerances. | |
| Symmetrical – application of two limit deviations, with which the dimension text is displayed with the same upper and lower limit deviations. The tolerance is separated from the dimension by the "±" symbol. The value is entered in the "Upper value" field. |
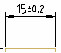
|
| Deviation – application of two limiting deviations. Dimension text is displayed with different upper and lower tolerance limits. When applying a dimension, a plus sign is put in front of the upper limit deviation and a minus sign in front of the lower one. |
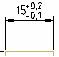
|
| Limits – displays dimension text as limit dimensions. The maximum size limit is above the minimum size limit. The largest limit is obtained by adding the upper limit deviation to the nominal size; the smallest - by subtracting the lower limit deviation from the nominal size. |
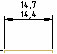
|
| Basic – displays the dimension text as a nominal boxed dimension. |
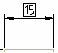
|
Precission - setting the number of decimal places after the decimal point.
Upper value - setting the value of the upper limit deviation. When the "Symmetrical" method is turned on, both deviations are assigned this value.
Lower value - setting the value of the lower limit deviation.
Scaling for height - setting the current text height for deviations.
Vertical position - alignment of deviation texts:
- Bottom - alignment of deviation and nominal size on the bottom.
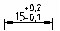
- Middle - aligning deviation and nominal size to the middle of the dimension text.
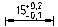
- Top - alignment of deviation and nominal size at the top.
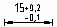
Zero suppression - control of suppression of leading and trailing zeros.
- Leading – suppress leading zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 0.3000 is written as .3000.
- Trailing – suppress trailing zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 11.5000 is represented as 11.5 and 30.0000 is represented as 30.
Alternate units tolerance
Alternative unit tolerance formatting.
Precision - setting the number of decimal places after the decimal point.
Zero suppression - control of suppression of leading and trailing zeros.
- Leading – suppress leading zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 0.3000 is written as .3000.
- Trailing – suppress trailing zeros in all decimal sizes. Example: 11.5000 is represented as 11.5 and 30.0000 is represented as 30.


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt 
