-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Exploding a Cloud into Points
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Exploding a Cloud into Points
Triangular Irregular Networks (TIN) have been used in GIS for many years and are a way to digitally represent surface structure. TIN is a form of vector digital geographic data that is constructed by triangulating a set of vertices (points). The vertices are connected by a number of edges to form a network of triangles. There are various interpolation methods for forming these triangles, such as Delaunay triangulation.
The surfaces created can be represented by such objects as SubDMesh, PolyFaceMesh, a collection of Solids, or a collection of 3D Faces.
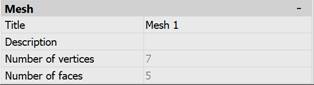
The properties of SubDMesh and PolyFaceMesh objects can be edited in the Properties bar. The Title and Description properties are available for editing. When copying an object, its Title and Description fields are also copied to the new object. The Number of vertices and Number of faces properties are informational.
 Ribbon: Topoplan – Create TIN >
Ribbon: Topoplan – Create TIN >  Explode the Cloud into Points
Explode the Cloud into Points
 Menu: Topoplan – Create TIN >
Menu: Topoplan – Create TIN >  Explode the Cloud into Points
Explode the Cloud into Points
 Toolbar: Create TIN >
Toolbar: Create TIN >  Explode the Cloud into Points
Explode the Cloud into Points
 Command line: NG_EXPLODE_POINTCLOUD
Command line: NG_EXPLODE_POINTCLOUD
The command allows you to create Points or Geopoints or Blocks objects based on the cloud points for further creation of TIN surface by them (for example, by the Create TIN by Points)command.
Before using the Explode the Cloud into Points command, run the Drawing Units command. In the Insertion scale section, set the value in meters.
If the number of points in the cloud is more than 100000, the cloud will be split into Points objects, even if COGOPoints or Blocks are selected in the parameters.
The command options are set in the Properties toolbar.
Options:
|
Result type |
Objects to be created based on the cloud points: Points, COGOPoints, Blocks. |
|
Delete source |
If Yes is selected – the source point cloud will be deleted after the split is completed. No – the source point cloud remains in the drawing. |
|
Use class |
If the cloud has been previously classified, it is possible to get only points of the specified class after splitting. |
Command prompts:
|
Apply changes? <Yes> or [Yes/No]: |
Yes – split into points will be made with the current settings. No – if the settings have been changed, they are not saved. Split into points will be made with the settings displayed immediately after starting the command. |
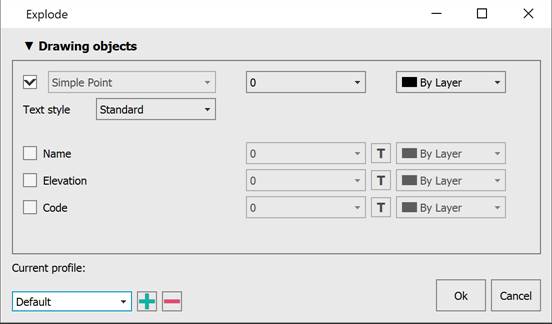
Then the Explode dialog box appears.
If a Geopoint object is selected, the layers will be locked.
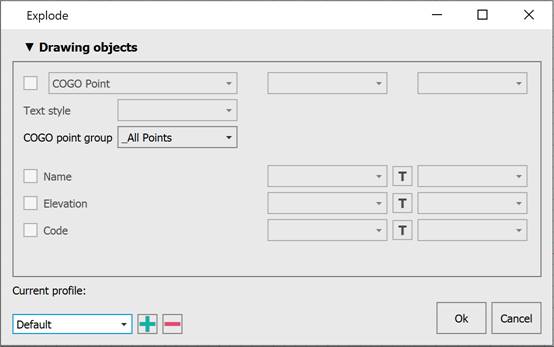
Options:
|
Drawing objects |
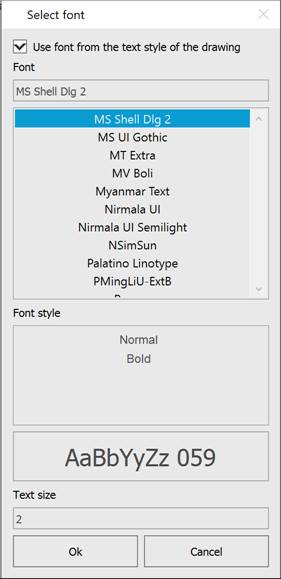
The section defines what components will be displayed for points on the screen: Marker, Name, Elevation (Z-coordinate), Code (point description). Each component can be assigned its own layer, color, and signatures - a font. The Select font dialog allows you to change the name, style and height. Or use a font from the drawing text style.
You can also specify the text style for the Marker.
|
|
|
|
|
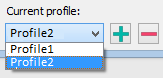
Current profile |
Allows you to save all the settings made in the dialog to a profile for later use.
|
When splitting, a group with a name corresponding to the name of the cloud is created. After the cloud is broken down into points, the points take on the color of the cloud (the current cloud display mode).
note: If a cloud being broken has more than 100000 points, the process may take a long time .


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt