-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Construction lines
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Construction lines
 Main menu: Mechanical - Utilities - Construction lines.
Main menu: Mechanical - Utilities - Construction lines.
 Ribbon: Mechanical - Utilities - Construction lines.
Ribbon: Mechanical - Utilities - Construction lines.
 Toolbar: "Construction lines".
Toolbar: "Construction lines".

Auxiliary lines are characterized by a layer in which they are placed by default (MCSCLines), color (red) and line type (thin solid), that are set in the settings. Additional settings - prostanovki rays or lines. Settings only apply to newly inserted objects. When you switch the existing objects remain as it is.
The table below describes which objects need to select and how formed auxiliary line in terms nanoCAD.
Some commands allow you to specify a sequence of auxiliary lines in the format XX|XX|XX, where XX - the amount of displacement of the beam (direct) in degrees or drawing units from the base position or previous beam, rendered in this command.
| Command | Name | The algorithm works command | Objects of choice | |
| When drawing rays (_ray) | When drawing lines (_xline) | |||
 Mcconsthor Mcconsthor
|
Create a horizontal auxiliary line |
Command is invoked _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. The second point is determined by the program to define the orientation of the beam is strictly horizontal. Point is determined by the positive direction of the X axis.
Option R-Turn-ray-to-180-degrees allows you to change the direction of the beam on the opposite |
Command is invoked _xline, in which the user is given the insertion point. The second point is determined by the program to define the orientation of the line is strictly horizontal. | Insertion point |
 Mcconstver Mcconstver
|
Creating vertical reference line |
Command is invoked _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. The second point is determined by the program to define the orientation of the beam is strictly vertical. Point is determined by the positive direction of the axis Y.
Option Rotate-ray-through-180-degrees allows you to change the direction of the beam on the reverse. |
Command is invoked _xline, in which the user is given the insertion point. The second point is determined by the program to define the orientation of the line is strictly vertical. | Insertion point |
 Mcconstz Mcconstz
|
Create an auxiliary line in the direction Z |
Command is invoked _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. Constructed beam emerging from this point in the positive direction OZ.
Option Rotate-ray-through-180-degrees allows you to change the direction of the beam on the reverse. |
Insertion point | |
 Mcconstcrs Mcconstcrs
|
Creating auxiliary lines intersecting |
Command is invoked _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. Built at the intersection of the rays of the insertion point in the positive direction of the axes OX and OY. Options allow you to select the quadrant bounded by the rays. |
Command is invoked _xline, in which the user is given the insertion point. Constructed lines intersect at the insertion point. | Insertion point |
 Mcconsthb Mcconsthb
|
Create an auxiliary line by two points or corner | Command is invoked _ray,in which the user is given the insertion point. Then to complete the command inserted rays at a predetermined angle with respect to OX (angle determined by the second point specified by the user) or a number of angles for group insert format XX | XX | XX. | Command is invoked _xline, in which the user is given the insertion point. Then to complete the command inserted straight with a predetermined angle with respect to OX (angle determined by the second point specified by the user) or a number of angles for group insert format XX | XX | XX. | Insertion point, a point which determines the angle (angle) or entering a number. The command completed after entering the series or after the forced shutdown command (Esc or right button). |
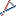 Mcconsthw Mcconsthw
|
Create an auxiliary line at an angle to the segment | Command is invoked _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. Specifies the position of the base angle (line). Then to complete the command inserted rays at a predetermined angle relative to the base angle or angles for a number of bulk-insert format XX | XX | XX. The angle is determined by the user of said second point. | Command is invoked _xline, in which the user is given the insertion point. Specifies the position of the base angle (line). Then to complete the command inserted straight with a predetermined angle relative to the base angle or angles for a number of bulk-insert format XX | XX | XX. The angle is determined by the user of said second point. | Insertion point, the point defining the base angle (or segment), which determines the point angle (angle) or entering a number. The command completed after entering the series or after the forced shutdown command (Esc or right button). |
 Mcconstpar Mcconstpar
|
Creating an auxiliary line parallel at a predetermined distance | Command is invoked_ray, in which the user selects a segment, polyline, line or ray. Further, given the parallel position of the object as a point through which it must pass (in the case of a polyline - equidistant) or number of copies of an object in the format XX | XX | XX. | Command is invoked _xline, in which the user selects a segment, polyline, line or ray. Further, given the parallel position of the object as a point through which it must pass (in the case of a polyline - equidistant) or number of copies of an object in the format XX | XX | XX. | Beam line, polyline or line. Reference point or enter a number. The command completed after entering the series or after the forced shutdown command (Esc or right button). |
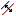 Mcconstpar2 Mcconstpar2
|
Creation of a parallel auxiliary line at half the specified distance | Command is invoked _ray, in which the user selects a segment, polyline, line or ray. Further, given the parallel position of the object as a point through which it must pass (in the case of a polyline - equidistant) or number of copies of an object in the format XX | XX | XX. The resulting objects are at half of the distance. | Command is invoked _xline, in which the user selects a segment, polyline, line or ray. Further, given the parallel position of the object as a point through which it must pass (in the case of a polyline - equidistant) or number of copies of an object in the format XX | XX | XX. The resulting objects are at half of the distance. | Beam line, polyline or line. Reference point or enter a number. The command completed after entering the series or after the forced shutdown command (Esc or right button). |
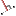 Mcconstlot2 Mcconstlot2
|
Establishment of a subsidiary of the perpendicular by two points | Command is _ray, in which the user is given the insertion point. Then, the user specifies the second point (a preview is rendered beam and segment coming from the insertion point, the second point is tied to the cursor) to specify the second point forms perpendicular to the beam. Ray is drawn perpendicular to the object. | Command is invoked _xline, that sets the insertion point. Then, the user specifies the second point (a preview is rendered straight and cut coming from the insertion point, the second point is tied to the cursor) to specify the second point forms perpendicular to the line. Direct drawn perpendicular to the object. | Insertion point, reference point on the perpendicular to the object renders. |
 Mcconstlot Mcconstlot
|
Create an auxiliary line perpendicular to the segment | Command is invoked _ray, for which the user selected reference object and point to it. Ray is drawn perpendicular to this object at the selected point. Starting beam is at a selected point. | Command is invoked _xline, , in which the user selects the object and reference point on it. Direct drawn perpendicular to this object at the selected point. Middle line is the selected point. | Beam line, polyline or line. Point on the object. |
 Mcconsthm Mcconsthm
|
Create an auxiliary line to the corner along the bisector | Command is invoked _ray, for which the user selects two reference object. Ray is based on the bisector between the two reference objects. | Command is invoked _xline,in which the user selects two reference object. Direct built along the bisector between the two reference objects. | Beam line, polyline or line. |
 Mcconsttan Mcconsttan
|
Create two parallel auxiliary lines tangent to the circle | Selected circle or arc that it may determine. Constructed two rays tangent to the circle, it is necessary to ask a series of positioning angles or point specified segment emanating from the center of the circle and parallel rays (link). | Selected circle or arc that it may determine. Constructed two lines tangent to the circle, it is necessary to ask a series of positioning angles or point specified segment emanating from the center of the circle and parallel lines (link). | Circle or arc. |
 Mcconstcc Mcconstcc
|
Creating auxiliary circle another circle concentric circle or arc is selected. | Automatically construct a circle concentric with the selected object and specify the diameter (or the given number of diameters). The command completed after entering the series or after the forced shutdown command (Esc or right button). | Circle or arc. | |
 Mcconstc2 Mcconstc2
|
Creating auxiliary circle tangent to the segment | Selected reference line object, the user specifies a point lying on the circle defined by the radius of the circle (the system offers the minimum possible radius which is equal to half the distance along the normal from the selected point to the segment, and controls the maintenance of value (greater or equal)). We construct a circle at two points of tangency (one point is given conditional perpendicular) and radius.. | Beam line, polyline or line. Point belonging to the circle. | |
 Mcconstkr Mcconstkr
|
Creating auxiliary circle tangent to two segments | Selected two reference linear object and specify the diameter. We construct a circle at two points of tangency and radius. | Beam line, polyline or line. | |
 Mcconstkr Mcconstkr
|
Creating auxiliary circle tangent to three segments | Selected two reference linear object. We construct a circle at three points of tangency.The radius is calculated automatically. | Beam line, polyline or line. | |
 Mcconstcircli Mcconstcircli
|
Creating auxiliary square circumscribing circle | Selected circle or arc, automatically builds a square, a circle is described. The context menu provides switching between inscribed and described by the square. | Circle arc. | |
 Mcconsttc Mcconsttc
|
Create an auxiliary line tangent to two circles | Selected consecutively two arcs or circles. Constructed beam tangent to the two circles, a definite choice (touch point - coming to a place of choice, the beginning of the beam - the first object). | Selected consecutively two arcs or circles. Constructed line tangent to the two circles, a definite choice (touch point - coming to a place of choice, the center line - the first object). | Two arcs or circles |
 Mcconst_circle Mcconst_circle
|
Creating auxiliary circle | This is the counterpart nanoCAD assigning properties auxiliary geometry. | ||
 Mcconstxray Mcconstxray
|
Creating a subsidiary of rays emanating from a single point | This is the counterpart nanoCAD assigning properties auxiliary geometry. | ||
 Mcconstxline Mcconstxline
|
Creating auxiliary lines passing through one point | This is the counterpart nanoCAD assigning properties auxiliary geometry. | ||
 Mcconstlines Mcconstlines
|
Auxiliary lines | This command displays the settings nanoCAD Mechanica with a pointer to the section Auxiliary lines. | ||
 Mcclineo Mcclineo
|
Enable / disable the auxiliary lines | This command automatically hides all auxiliary lines. | ||
 Mcconsterase Mcconsterase
|
Remove auxiliary lines | This command automatically removes all auxiliary lines. | ||


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt 

