-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Classification of Cloud Points
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Classification of Cloud Points
Classification commands change the Class attribute for points of the cloud for convenience of further processing.
General Principle of Classification Commands
Classification commands work as follows:
· Defining source point classes;
· Defining the destination class;
· Specifying points accordance to criteria used by the started classification command.
Presence of Class attribute in cloud points
If during import the cloud did not have Class attribute, when trying to classify points of such cloud, a message will appear in the command line:
Selected point clouds has no Class attribute, to be able to use classification procedures, you must switch on it
In this case, it is necessary to create Class attribute for cloud points. To do this, in the Storage structure section of the Point Cloud Statistics dialog
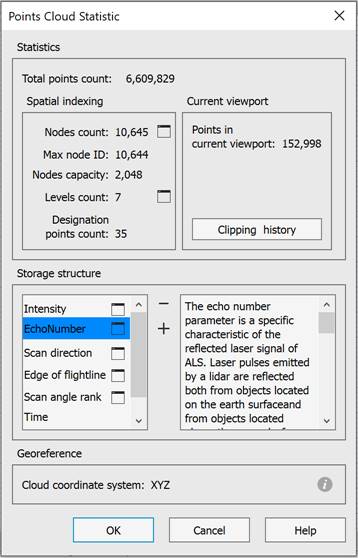
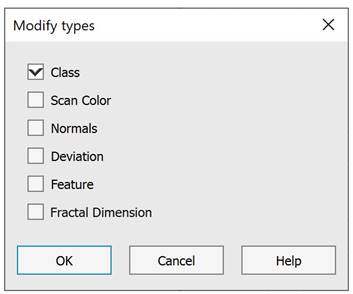
click the  button, followed by selection from the list in the Modify types dialog.
button, followed by selection from the list in the Modify types dialog.
check the Class box.
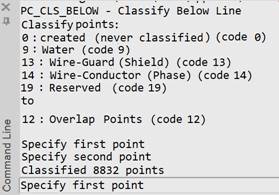
Output information in the command line
If the source and destination classes are correctly specified, when any of the classification commands are called (after selecting the command options), a message will appear:
Classify points:
|
- the command line will display the source classes and their codes. - the command line will also display the target class into which the points will be classified. After the classification is complete, a message will appear: Classified N points Where N is the number of points which were classified. |
|


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt