Raster Features
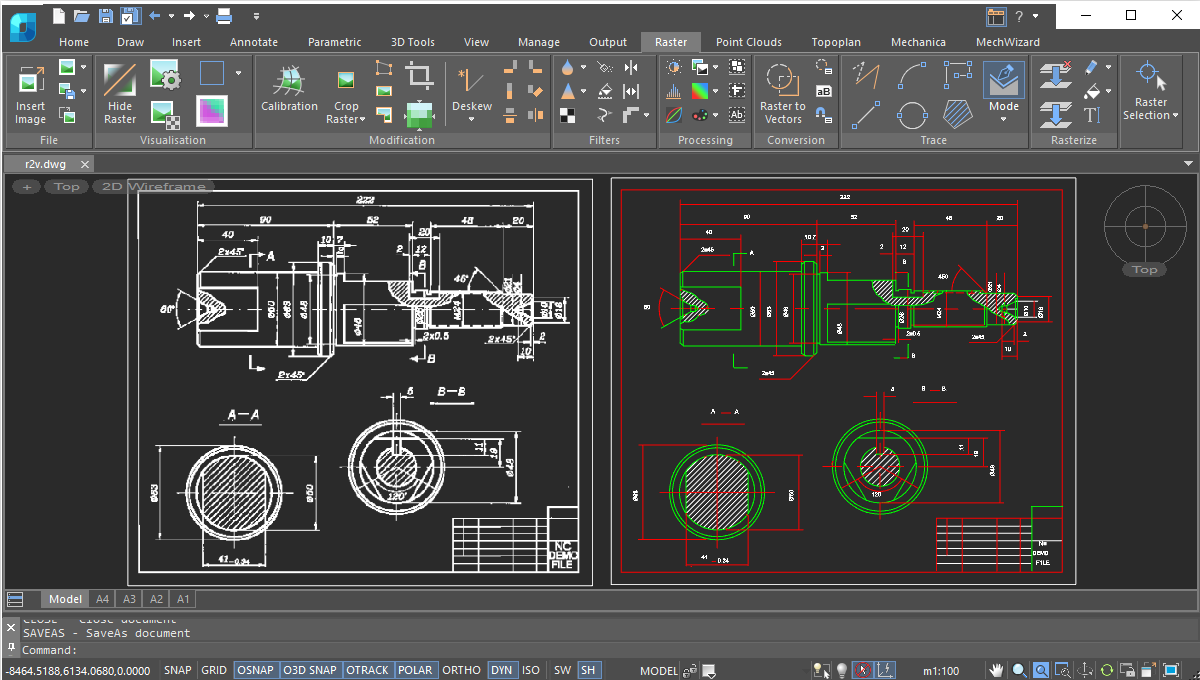
Automatic vectorization
The Raster Module converts raster images into the vector objects by recognizing the following entities: points, lines, arcs, circles, hatches, texts, symbols, and outlines. At the end of the vectorization process, lines, circles, arcs, polylines, and arrowheads are recognized as object types.
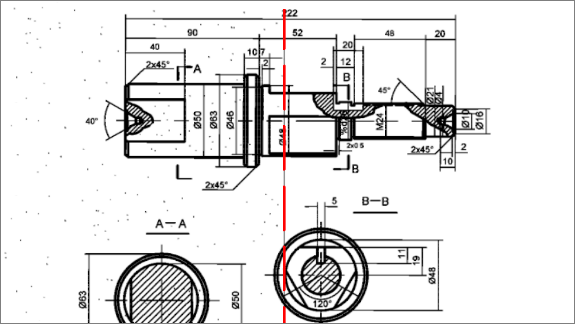
Monochrome filtering
The Raster Module offers a rich variety of monochrome filters, such as smoothing, thinning and thickening, removing speckles, filling holes, generating contours, and inverting images. These not only improve image quality, but also reduce the size of raster files significantly.
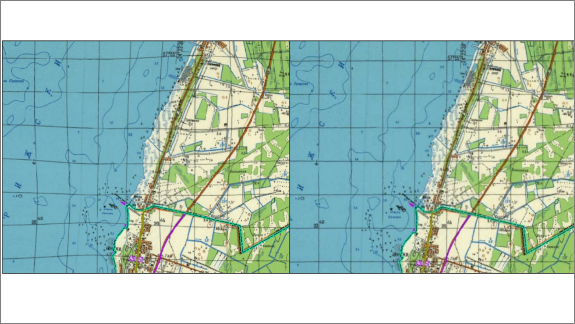
Correcting image geometry
The Raster Module corrects geometric distortions in raster images, whether monochrome, grayscale, or color:
- Resizing raster images
- Scaling images and changing resolutions
- Cropping
- Deskewing
- Mirroring along vertical or horizontal axes
- Rotating to any angle
- Correcting trapezoidal, parallelogram, and projection distortions through four-point correction
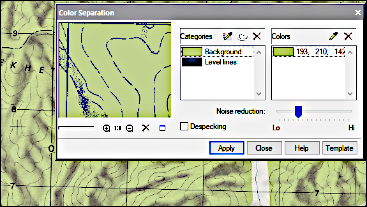
Color reduction and separation
The Raster Module separates objects of different colors (such as roads and rivers) onto their own monochrome layers. The efficiency obtained in using this technique is higher than by making black-and-white scans of color images.
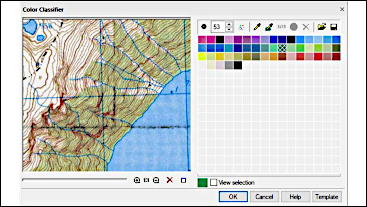
Color correction
The Raster Module’s color correction tools prepare images for subsequent complex operations, such as editing, slicing, and raster-to-vector conversion:
- True color conversion
- Grayscale conversion
- Indexed colors conversion
- Brightness, contrast, hue, and saturation adjustments
- Histogram correction
- Gamma correction
- Color palette editing (color classifier)
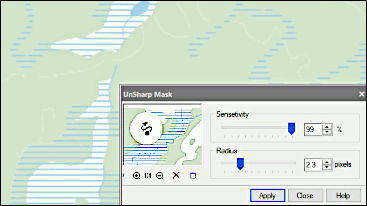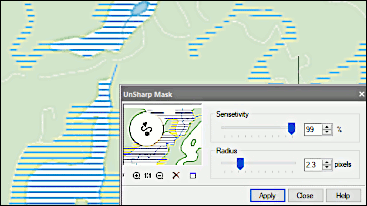
Color filtering
The Raster Module’s color filtering tools prepare images for subsequent operations. Color filtering improves the quality of images after operations that move entities in the image or change the resolution through scaling, alignment, rotation, calibration, and four-point correction. Tools in color filtering include the following:
- Adaptive Blur
- Blur
- Contour sharpness
- Median
Semi-automatic tracing
The Raster Module vectorizes raster images of any type through tracing. it also smoothes and removes artifacts from monochrome images.
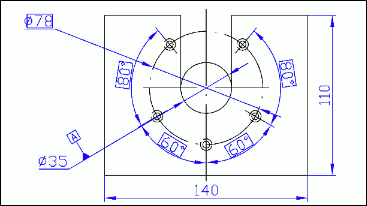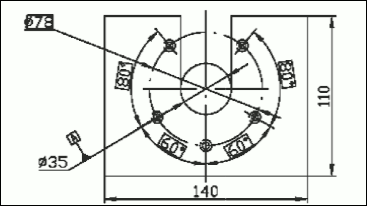
Rasterization
The Raster Module rasterizes and merges selected vector and raster data onto underlying raster images. The selection can consist of raster images or/and CAD objects.
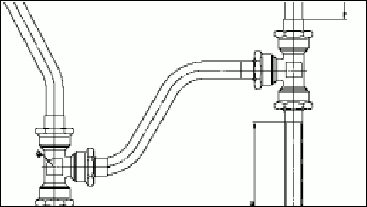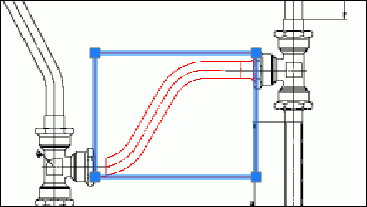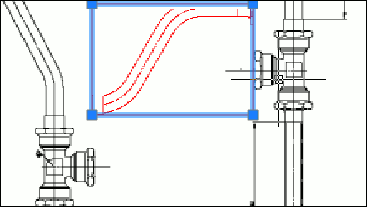
Raster image selections
The Raster Module selects the following portions of raster images and transfers them to new raster images on specified layers:
- Areas of raster images
- Multiple interconnected raster points
- Raster lines segments of any shape defined by intersections with other raster lines or by endpoints
- Raster entities, such as raster lines, arcs and circles


 De
De  Es
Es  Fr
Fr  Pt
Pt 
